179 在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先(再进阶)
ac
Tarjan算法与并查集解决批量查询【在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先】
query: 4 (7 7 (8 2 (8 9 1 / \ 2 3 / \ \ 4 5 6 / \ / 7 8 9 遍历到4,发现有7,但是7没有遍历到 遍历到2,{2} 和 {4} 结合{2, 4} fa为 2 {5, 7} fa为 5 {5, 7, 8} fa为 5 {2, 4, 5, 7, 8} 祖先为2
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; class TreeNode{ TreeNode left; TreeNode right; int val; public TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; left = null; right = null; } } class Query{ TreeNode o1; TreeNode o2; public Query(TreeNode o1, TreeNode o2) { this.o1 = o1; this.o2 = o2; } } class DisjointSets{ Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> fatherMap;// 存根 Map<TreeNode, Integer> rankMap; // 秩 public DisjointSets() { this.fatherMap = new HashMap<>(); this.rankMap = new HashMap<>(); } void makeSets(TreeNode head){ fatherMap.clear(); rankMap.clear(); preOrderMake(head); } void preOrderMake(TreeNode head){ if(head == null){ return; } // 根都是自己,秩都是0 fatherMap.put(head, head); rankMap.put(head, 0); preOrderMake(head.left); preOrderMake(head.right); } public TreeNode findFa(TreeNode n){ TreeNode fa = fatherMap.get(n); if(fa != n){ fa = findFa(fa); } fatherMap.put(n, fa); return fa; } public void union(TreeNode a, TreeNode b){ if(a == null || b == null){ return; } TreeNode aFa = findFa(a); TreeNode bFa = findFa(b); if(aFa != bFa){ int aRank = rankMap.get(aFa); int bRank = rankMap.get(bFa); if(aRank < bRank){ fatherMap.put(aFa, bFa); // aFa 接到 bFa下面,bFa作为父根,即秩大的作为根 }else if(aRank > bRank){ fatherMap.put(bFa, aFa); }else { fatherMap.put(bFa, aFa); rankMap.put(aFa, aRank + 1); } } } } class TarJan{ Map<TreeNode, LinkedList<TreeNode>> queryMap; Map<TreeNode, LinkedList<Integer>> indexMap; Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> ancestorMap; DisjointSets sets; public TarJan() { // 临接表,key为查询涉及的某个节点,value是个链表 queryMap = new HashMap<>(); // key为查询涉及的某个节点,value是个链表,表示设置的结果位置 indexMap = new HashMap<>(); ancestorMap = new HashMap<>(); sets = new DisjointSets(); } public TreeNode[] query(TreeNode head, Query[] queries){ TreeNode[] ans = new TreeNode[queries.length]; setQueries(queries, ans); // 初始化并查集 sets.makeSets(head); // 设置结果 setAnswers(head, ans); return ans; } public void setQueries(Query[] ques, TreeNode[] ans){ TreeNode o1 = null; TreeNode o2 = null; for(int i=0;i<ques.length;i++){ o1 = ques[i].o1; o2 = ques[i].o2; if(o1 == o2 || o1 == null || o2 == null){ ans[i] = o1 != null ? o1 : o2; }else { if(!queryMap.containsKey(o1)){ queryMap.put(o1, new LinkedList<>()); indexMap.put(o1, new LinkedList<>()); } if(!queryMap.containsKey(o2)){ queryMap.put(o2, new LinkedList<>()); indexMap.put(o2, new LinkedList<>()); } queryMap.get(o1).add(o2); indexMap.get(o1).add(i); queryMap.get(o2).add(o1); indexMap.get(o2).add(i); } } } public void setAnswers(TreeNode head, TreeNode[] ans){ if(head == null){ return; } setAnswers(head.left, ans); sets.union(head.left, head); ancestorMap.put(sets.findFa(head), head); setAnswers(head.right, ans); sets.union(head.right, head); ancestorMap.put(sets.findFa(head), head); // 看查询中是否有有与node相关的,queryMap 和 indexMap 获取 LinkedList<TreeNode> nList = queryMap.get(head); LinkedList<Integer> iList = indexMap.get(head); while (nList != null && ! nList.isEmpty()){ // 取头部元素,求的是 node 和 head 的公共节点 TreeNode node = nList.poll(); // 原始 query 的 index int index = iList.poll(); TreeNode nodeFa = sets.findFa(node); if(ancestorMap.containsKey(nodeFa)){ ans[index] = ancestorMap.get(nodeFa); } } } } public class Main { public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); public static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); public static long mod = (long) Math.pow(2, 29); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String line; String[] strArr; line = reader.readLine(); strArr = line.split(" "); int n = Integer.valueOf(strArr[0]); int rootVal = Integer.valueOf(strArr[1]); Map<Integer, TreeNode> mp = new HashMap<>(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { line = reader.readLine(); strArr = line.split(" "); int val = Integer.valueOf(strArr[0]); int leftVal = Integer.valueOf(strArr[1]); int rightVal = Integer.valueOf(strArr[2]); if (!mp.containsKey(val)) { mp.put(val, new TreeNode(val)); } if (leftVal != 0) { if (!mp.containsKey(leftVal)) { mp.put(leftVal, new TreeNode(leftVal)); } mp.get(val).left = mp.get(leftVal); } if (rightVal != 0) { if (!mp.containsKey(rightVal)) { mp.put(rightVal, new TreeNode(rightVal)); } mp.get(val).right = mp.get(rightVal); } } TreeNode root = mp.get(rootVal); n = Integer.valueOf(reader.readLine()); Query[] queries = new Query[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { line = reader.readLine(); strArr = line.split(" "); int p = Integer.valueOf(strArr[0]); int q = Integer.valueOf(strArr[1]); queries[i] = new Query(mp.get(p), mp.get(q)); } TreeNode[] ans = tarJanQuery(root, queries); // 打印结果 for(int i=0;i<ans.length;i++){ System.out.println(ans[i].val); } } static TreeNode[] tarJanQuery(TreeNode head, Query[] queries){ TreeNode[] ans = new TarJan().query(head, queries); return ans; } } /* 1 / \ 2 3 / \ / \ 4 5 6 7 / 8 8 1 1 2 3 2 4 5 4 0 0 5 0 0 3 6 7 6 0 0 7 8 0 8 0 0 4 4 5 5 2 6 8 5 8 2 2 3 1 */
并查集
66题《并查集的实现》
Tarjan算法
-
无向图中,从i能到达j,则称i,j连通
-
如果两个顶点可以相互通达,则称两个顶点强连通(strongly connected)。
-
如果有向图G的每两个顶点都强连通,称G是一个
强连通图。 -
有向图的极大强连通子图,称为
强连通分量(strongly connected components)。
tarjan算法简单例子图解法
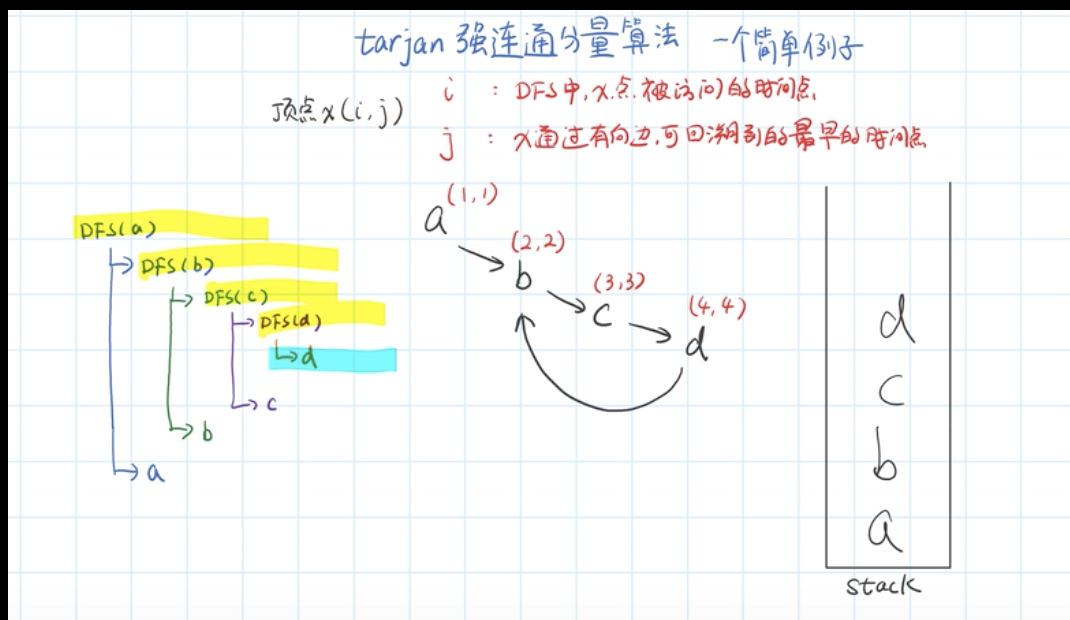
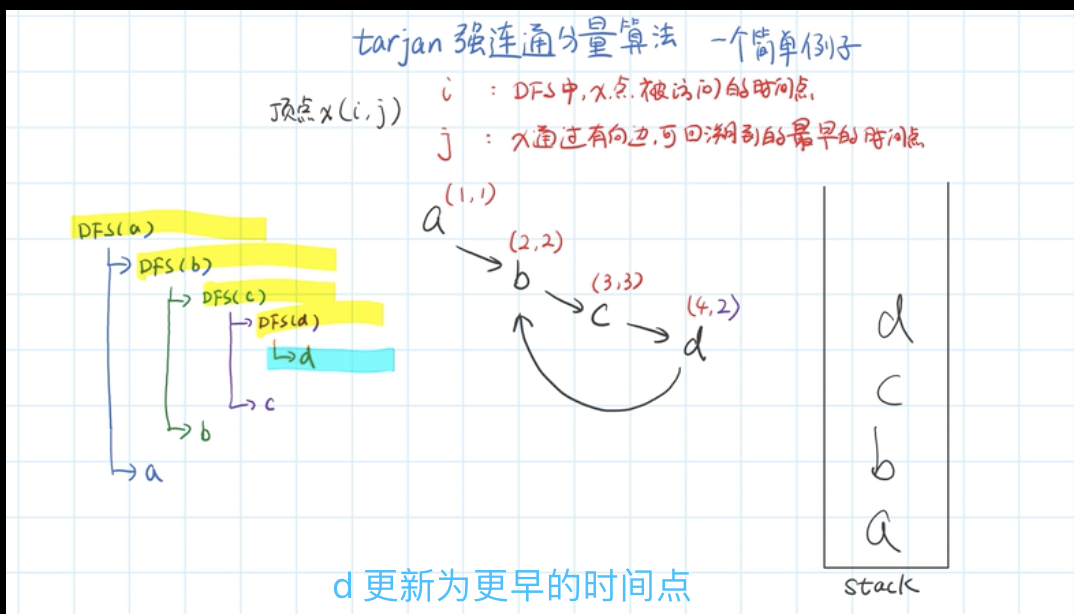
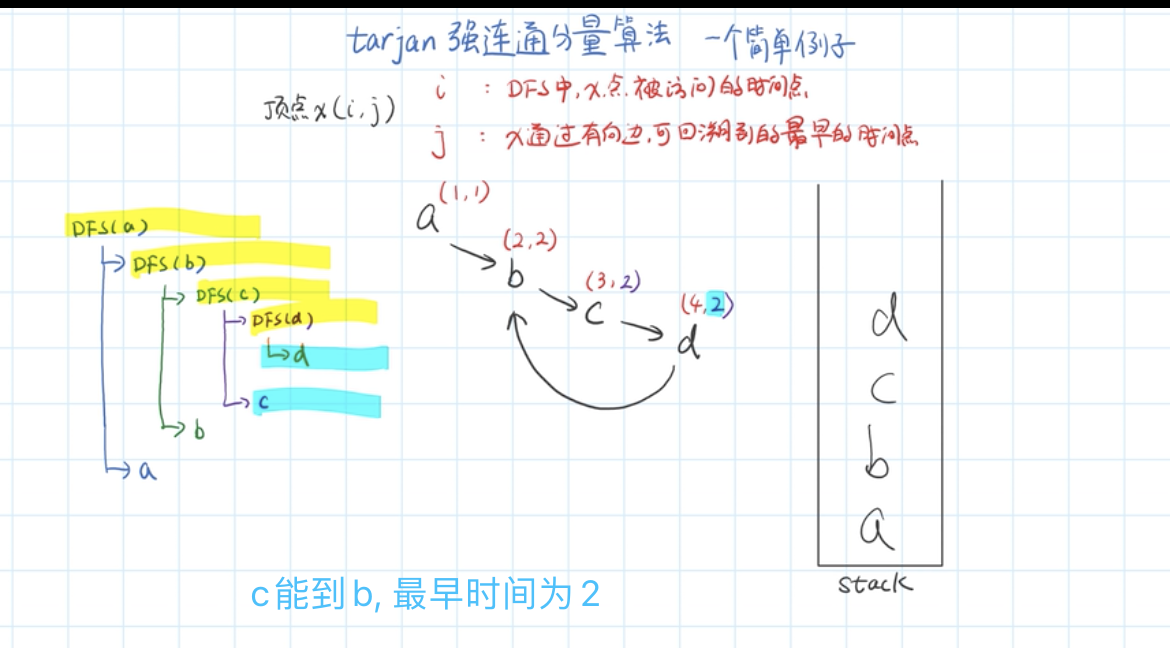
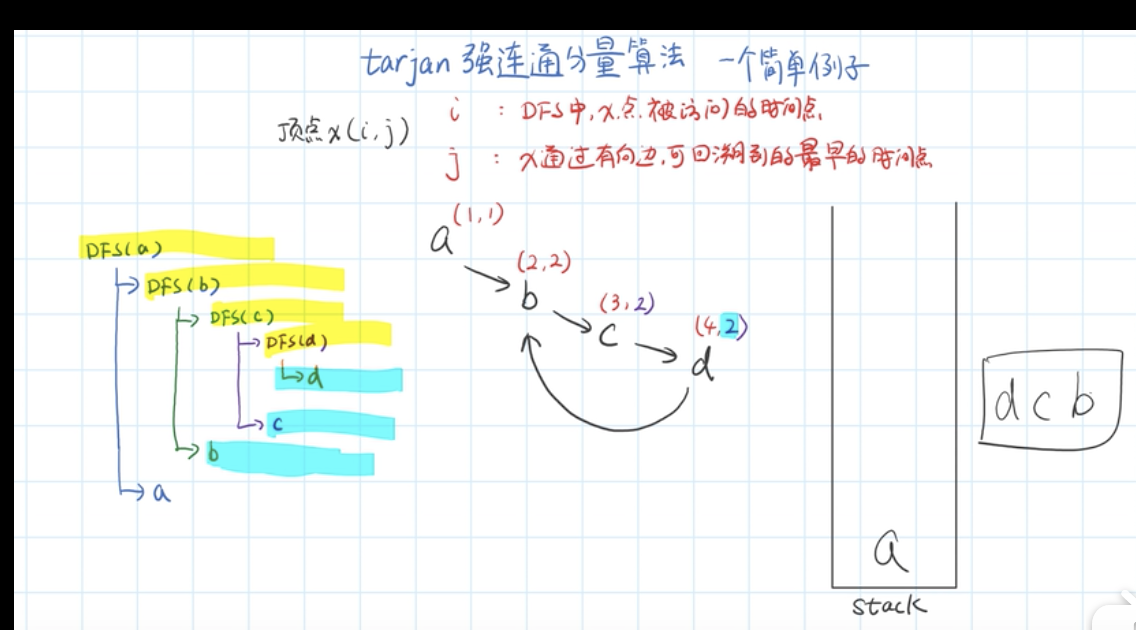
- 复杂点的
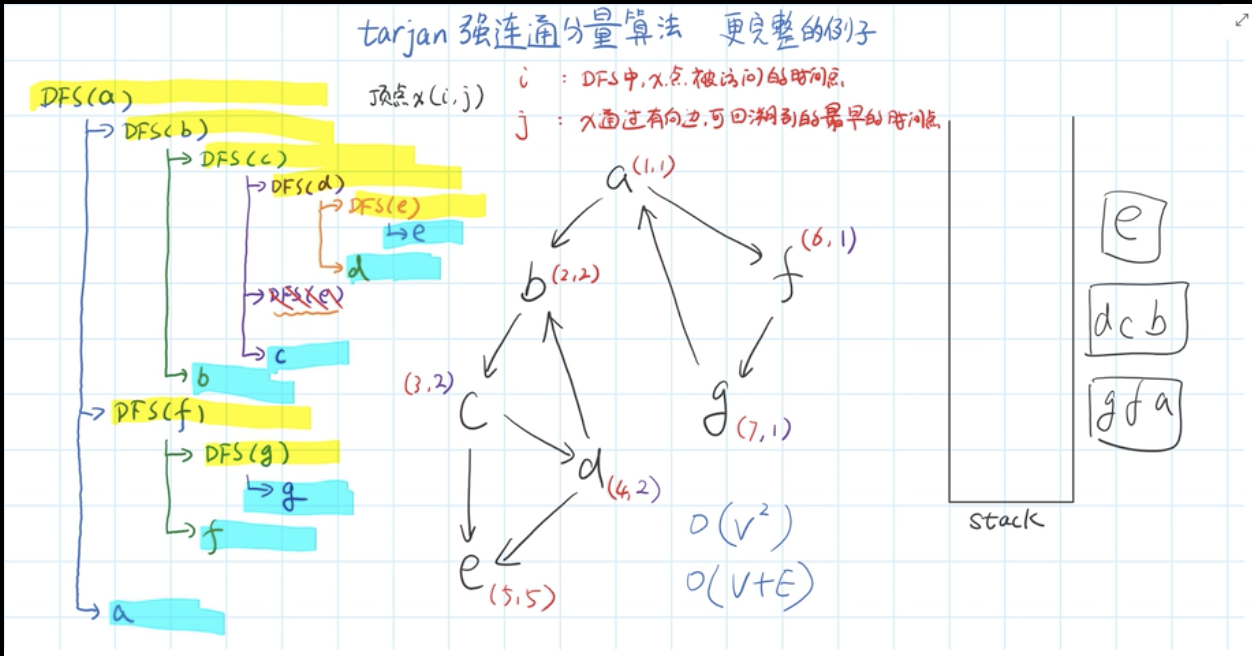
code编码
如下: 子图{1,2,3,4}为一个强连通分量,因为顶点1,2,3,4两两可达。{5},{6}也分别是两个强连通分量
1 ------> 3 -----> 5 | ^ | | | \ | | | \ | | V \ V V 2 -------> 4 -----> 6
Tarjan算法是基于对图深度优先搜索的算法,每个强连通分量为搜索树中的一棵子树。搜索时,把当前搜索树中未处理的节点加入一个堆栈,回溯时可以判断栈顶到栈中的节点是否为一个强连通分量
dfs方式1: 先输出自己,然后访问与自己相关的点,不断递归(类似先序)
dfs方式2: 访问完与自己相关的点,不断递归,再输出自己(类似后序)
- 定义
DFN(u)为节点u搜索的次序编号(时间戳),一旦某个点被DFS到后,这个时间戳就不再改变(且每个点只有唯一的时间戳) - 定义
Low(u)为u或u的子树能够追溯到的最早的栈中节点的次序号,Low[ ]相等的点相当于在一个强连通量上
则当DFN(u)=Low(u)时,以u为根的搜索子树上所有节点是一个强连通分量 - 初始时:dfn[ ] = low[ ] = ++count
4节点,最早回溯到1,1的次序是dfn[1] = 1, 所以,low[4] = 1
完整code
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.*; // 有向边 class Edge{ boolean inStack; // 是否栈中 List<Integer> next; } public class Main { public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); public static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); public static long mod = (long) Math.pow(2, 29); public static int N = 1001; static int[] dfn = new int[N]; static int[] low = new int[N]; static Edge[] edges = new Edge[N]; static void add(int u, int v){ if(edges[u] == null){ edges[u] = new Edge(); edges[u].next = new ArrayList<>(); } if(edges[v] == null) { edges[v] = new Edge(); edges[v].next = new ArrayList<>(); } edges[u].next.add(v); } static Stack<Integer> sta = new Stack<>(); static int count = 0; static void tarjan(int now){ dfn[now] = low[now] = ++ count; sta.push(now); edges[now].inStack = true; for(Integer v: edges[now].next){ if(dfn[v] <= 0){ // v 没有被访问过,递归 v tarjan(v); low[now] = Math.min(low[now], low[v]); // 回溯取最小,v是now的next }else if(edges[v].inStack){ // 在栈中, 则取其次序号dfn判断 low[now] = Math.min(low[now], dfn[v]); } } if(low[now] == dfn[now]){ int cur; do{ cur = sta.pop(); edges[cur].inStack = false; System.out.print(cur + " "); }while (cur != now); System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String line; String[] strArr; line = reader.readLine(); strArr = line.split(" "); int n = Integer.valueOf(strArr[0]); int num = Integer.valueOf(strArr[1]); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { line = reader.readLine(); strArr = line.split(" "); int u = Integer.valueOf(strArr[0]); int v = Integer.valueOf(strArr[1]); add(u, v); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(edges[i]!= null && edges[i].next != null && ! edges[i].next.isEmpty()) { Collections.sort(edges[i].next); } } tarjan(1); System.out.println(); } } /* 6 8 1 3 1 2 2 4 3 4 3 5 4 6 4 1 5 6 1 ------> 3 -----> 5 | ^ | | | \ | | | \ | | V \ V V 2 -------> 4 -----> 6 */
完整code2
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.*; // 有向边 class Edge{ boolean inStack; // 是否栈中 List<Integer> next; // 指向的节点 } public class Main { public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); public static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); public static long mod = (long) Math.pow(2, 29); public static int N = 1001; static int[] dfn = new int[N]; static int[] low = new int[N]; static Edge[] edges = new Edge[N]; static void add(int u, int v){ if(edges[u] == null){ edges[u] = new Edge(); edges[u].next = new ArrayList<>(); } if(edges[v] == null) { edges[v] = new Edge(); edges[v].next = new ArrayList<>(); } edges[u].next.add(v); } static Stack<Integer> sta = new Stack<>(); static int count = 0; static void dfs(int now){ // 访问并入栈 dfn[now] = low[now] = ++ count; sta.push(now); edges[now].inStack = true; // dfs遍历 for(Integer v: edges[now].next){ if(dfn[v] <= 0){ // v 没有被访问过,递归 v dfs(v); // 回溯,取最小的能回到的low low[now] = Math.min(low[now], low[v]); }else if(edges[v].inStack){ // 否则访问的是在栈中的,当前访问的看能否回到栈中最小的 low[now] = Math.min(low[now], low[v]); } } // 如果dfs 和 low 相等了,表示一个强联通分量构成 if(low[now] == dfn[now]){ int cur; do{ cur = sta.pop(); // 消除inStack, 但是dfs不消除 edges[cur].inStack = false; System.out.print(cur + " "); }while (cur != now); System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String line; String[] strArr; line = reader.readLine(); strArr = line.split(" "); int n = Integer.valueOf(strArr[0]); int num = Integer.valueOf(strArr[1]); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { line = reader.readLine(); strArr = line.split(" "); int u = Integer.valueOf(strArr[0]); int v = Integer.valueOf(strArr[1]); add(u, v); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(edges[i]!= null && edges[i].next != null && ! edges[i].next.isEmpty()) { Collections.sort(edges[i].next); } } dfs(1); System.out.println(); } } /* 6 8 1 3 1 2 2 4 3 4 3 5 4 6 4 1 5 6 6 5 3 4 2 1 */