TreeviewCopyright @doctording all right reserved, powered by aleen42
@Transactional
事务的传播特性
什么是事务的传播特性?
指的是当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法该如何进行?
@Transactional
public void A(){
// xx
B();
C();
// xx
// 出现异常
}
@Transactional
public void B(){
// xx
// 出现异常
}
@Transactional
public void C(){
// xx
// 出现异常
}
如上:事务A内部有事务B,事务C;如果A异常了,那么B,C怎么处理事务;如果B,C事务异常,那么事务A怎么处理?
Spring给出的7种事务的传播类型
/**
* Enumeration that represents transaction propagation behaviors for use
* with the {@link Transactional} annotation, corresponding to the
* {@link TransactionDefinition} interface.
*
* @author Colin Sampaleanu
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 1.2
*/
public enum Propagation {
/**
*
* Support a current transaction, create a new one if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>This is the default setting of a transaction annotation.
*/
REQUIRED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED),
/**
* Support a current transaction, execute non-transactionally if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>Note: For transaction managers with transaction synchronization,
* PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS is slightly different from no transaction at all,
* as it defines a transaction scope that synchronization will apply for.
* As a consequence, the same resources (JDBC Connection, Hibernate Session, etc)
* will be shared for the entire specified scope. Note that this depends on
* the actual synchronization configuration of the transaction manager.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setTransactionSynchronization
*/
SUPPORTS(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS),
/**
* Support a current transaction, throw an exception if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
*/
MANDATORY(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY),
/**
* Create a new transaction, and suspend the current transaction if one exists.
* Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box
* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},
* which requires the {@code javax.transaction.TransactionManager} to be
* made available it to it (which is server-specific in standard Java EE).
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager
*/
REQUIRES_NEW(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW),
/**
* Execute non-transactionally, suspend the current transaction if one exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box
* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},
* which requires the {@code javax.transaction.TransactionManager} to be
* made available it to it (which is server-specific in standard Java EE).
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager
*/
NOT_SUPPORTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED),
/**
* Execute non-transactionally, throw an exception if a transaction exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
*/
NEVER(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER),
/**
* Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists,
* behave like PROPAGATION_REQUIRED else. There is no analogous feature in EJB.
* <p>Note: Actual creation of a nested transaction will only work on specific
* transaction managers. Out of the box, this only applies to the JDBC
* DataSourceTransactionManager when working on a JDBC 3.0 driver.
* Some JTA providers might support nested transactions as well.
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
*/
NESTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED);
private final int value;
Propagation(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
}
| 传播属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| required(默认) | 如果存在一个事务,则支持当前事务。如果没有事务则开启一个新的事务。被设置成这个级别时,会为每一个被调用的方法创建一个逻辑事务域。如果前面的方法已经创建了事务,那么后面的方法支持当前的事务,如果当前没有事务会重新建立事务。 |
| requires_new | 不管当前是否已经存在事务,都会新建一个事务;开启的事务相互独立,互不干扰。 |
| Mandatory | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。 |
| Never | 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 |
| Not_supports | 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 |
| Supports | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。 |
| Nested | 支持当前事务,新增Savepoint点,与当前事务同步提交或回滚。嵌套事务一个非常重要的概念就是内层事务依赖于外层事务。外层事务失败时,会回滚内层事务所做的动作。而内层事务操作失败并不会引起外层事务的回滚。 |
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA() {
methodB();
// do something
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodB() {
// do something
}
- 单独调用methodB方法时,因为当前上下文不存在事务,所以会开启一个新的事务。
- 调用methodA方法时,因为当前上下文不存在事务,所以会开启一个新的事务。当执行到methodB时,methodB发现当前上下文有事务,因此就加入到当前事务中来。
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA() {
methodB();
// do something
}
// 事务属性为SUPPORTS
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public void methodB() {
// do something
}
- 单纯的调用methodB时,methodB方法是非事务的执行的。
- 当调用methodA时,methodB则加入了methodA的事务中,事务地执行。
Spring的5种事务隔离级别
/**
* Enumeration that represents transaction isolation levels for use
* with the {@link Transactional} annotation, corresponding to the
* {@link TransactionDefinition} interface.
*
* @author Colin Sampaleanu
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 1.2
*/
public enum Isolation {
/**
* 这是一个PlatformTransactionManager默认的隔离级别,使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别
*
* Use the default isolation level of the underlying datastore.
* All other levels correspond to the JDBC isolation levels.
* @see java.sql.Connection
*/
DEFAULT(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads
* can occur. This level allows a row changed by one transaction to be read by
* another transaction before any changes in that row have been committed
* (a "dirty read"). If any of the changes are rolled back, the second
* transaction will have retrieved an invalid row.
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED
*/
READ_UNCOMMITTED(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads
* and phantom reads can occur. This level only prohibits a transaction
* from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it.
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED
*/
READ_COMMITTED(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are
* prevented; phantom reads can occur. This level prohibits a transaction
* from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it, and it also prohibits
* the situation where one transaction reads a row, a second transaction
* alters the row, and the first transaction rereads the row, getting
* different values the second time (a "non-repeatable read").
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
*/
REPEATABLE_READ(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom
* reads are prevented. This level includes the prohibitions in
* {@code ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ} and further prohibits the situation
* where one transaction reads all rows that satisfy a {@code WHERE}
* condition, a second transaction inserts a row that satisfies that
* {@code WHERE} condition, and the first transaction rereads for the
* same condition, retrieving the additional "phantom" row in the second read.
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE
*/
SERIALIZABLE(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE);
private final int value;
Isolation(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
}
rollbackFor属性
/**
* Defines zero (0) or more exception {@link Class classes}, which must be
* subclasses of {@link Throwable}, indicating which exception types must cause
* a transaction rollback.
* <p>By default, a transaction will be rolling back on {@link RuntimeException}
* and {@link Error} but not on checked exceptions (business exceptions). See
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)}
* for a detailed explanation.
* <p>This is the preferred way to construct a rollback rule (in contrast to
* {@link #rollbackForClassName}), matching the exception class and its subclasses.
* <p>Similar to {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RollbackRuleAttribute#RollbackRuleAttribute(Class clazz)}.
* @see #rollbackForClassName
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)
*/
Class<? extends Throwable>[] rollbackFor() default {};
roll back默认是Error和RuntimeException
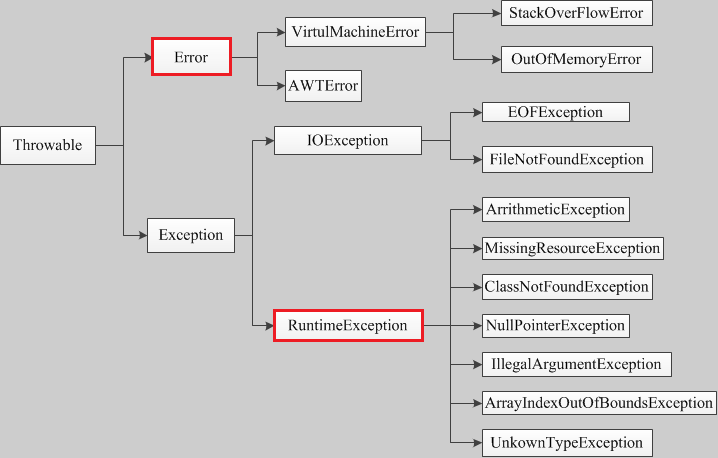
eg1: 不加rollbackFor属性,抛出RuntimeException,正常回滚
@Transactional
eg2: 不加rollbackFor属性,抛出IOException,不回滚
@Transactional
eg3: 加上rollbackFor = Exception.class,抛出IOException,正常回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
eg4: 不加rollbackFor属性,抛出OutOfMemoryError,正常回滚
@Transactional()
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
eg5: 加上rollbackFor = Exception.class,抛出OutOfMemoryError,正常回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();