TreeviewCopyright @doctording all right reserved, powered by aleen42
[TOC]
Future在规定时间内获取结果
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Main {
public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static SimpleDateFormat simpleFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/**
* 模拟sec秒延迟
*/
public static void delay(int sec) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sec);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Future<Double> getPrice(double df){
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<Double> future = executor.submit(new Callable<Double>() {
@Override
public Double call() throws Exception {
delay(5);
return df * 10;
}
});
executor.shutdown();
return future;
}
public static void priceTest(){
Future<Double> futurePrice = getPrice(10.0f);
Double price = null;
try{
price = futurePrice.get(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("cannot get within 1 sec");
boolean b = futurePrice.cancel(true);
System.out.println("cancel:" + b);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(price);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(simpleFormatter.format(new Date()));
priceTest();
System.out.println(simpleFormatter.format(new Date()));
}
}
超时获取输出
2019-11-02 15:14:47
cannot get within 1 sec
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
at Main.priceTest(Main.java:48)
at Main.main(Main.java:55)
Caused by: java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:205)
at Main.priceTest(Main.java:44)
... 1 more
Process finished with exit code 1
Future规定时间未获取到,中断处理
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.MoreExecutors;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Main {
public static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static SimpleDateFormat simpleFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/**
* 模拟sec秒延迟
*/
public static void delay(int sec) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sec);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Future<Double> getPrice(double df){
// ExecutorService executor = MoreExecutors.newDirectExecutorService();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
System.out.println(simpleFormatter.format(new Date()));
Future<Double> future = executor.submit(new Callable<Double>() {
@Override
public Double call() throws Exception {
delay(5);
return df * 10;
}
});
System.out.println(simpleFormatter.format(new Date()));
// executor.shutdown();
return future;
}
public static void priceTest(){
Future<Double> futurePrice = getPrice(10.0f);
Double price = null;
try {
price = futurePrice.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}catch (TimeoutException e){
System.out.println("cannot get within 1 sec");
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
// 取消执行
// futurePrice.cancel(true);
}catch (Exception e){
futurePrice.cancel(false);
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(price);
try {
price = futurePrice.get();
}catch (Exception e){
}
System.out.println(price);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(simpleFormatter.format(new Date()));
priceTest();
System.out.println(simpleFormatter.format(new Date()));
}
}
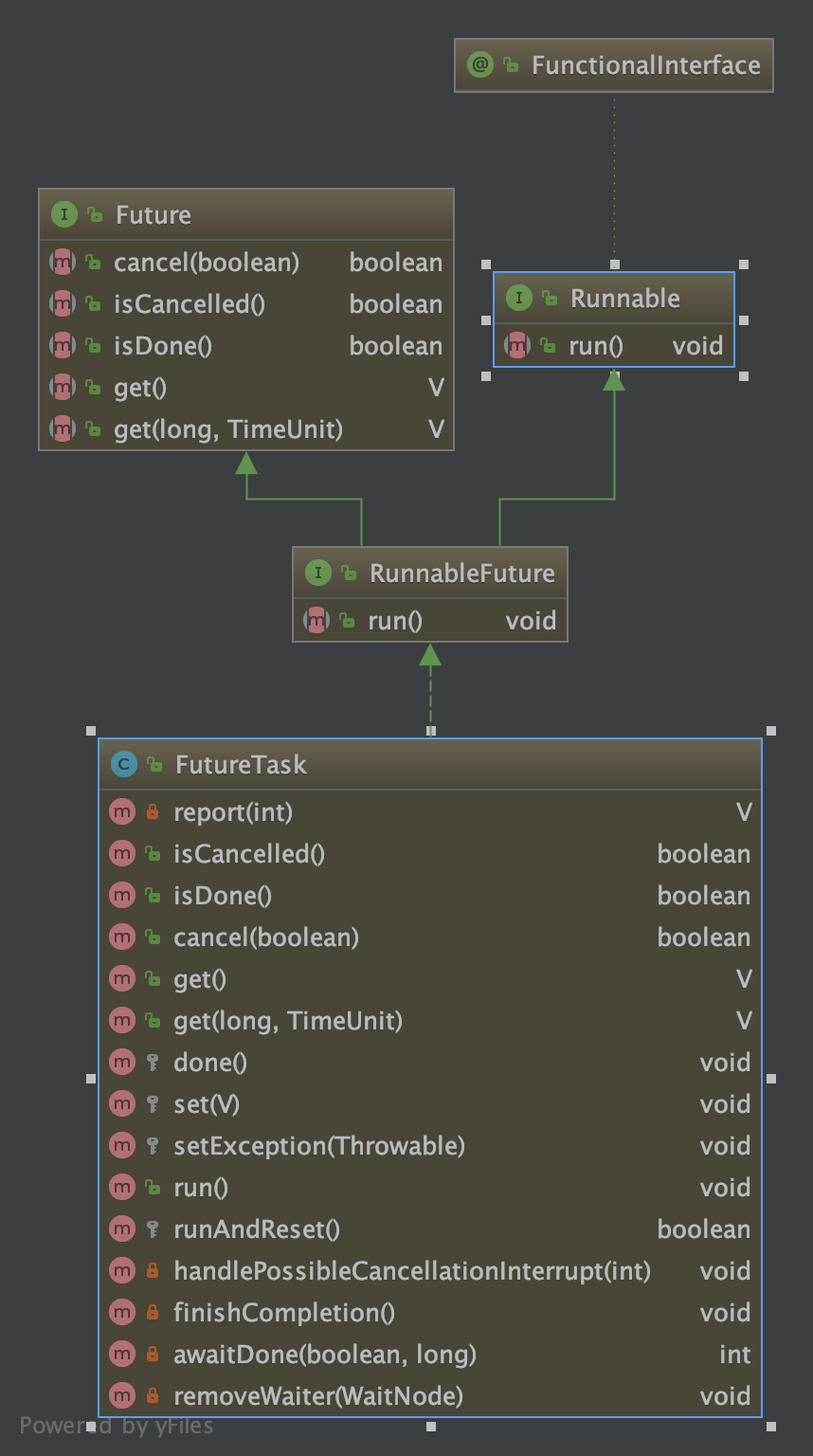
Callable、Future、FutureTask
- Runnable
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}
- Callable
可以有返回值,范型设置返回值类型;无法完成计算,可以抛出异常
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}
- Future
/**
* A {@code Future} represents the result of an asynchronous
* computation. Methods are provided to check if the computation is
* complete, to wait for its completion, and to retrieve the result of
* the computation. The result can only be retrieved using method
* {@code get} when the computation has completed, blocking if
* necessary until it is ready. Cancellation is performed by the
* {@code cancel} method. Additional methods are provided to
* determine if the task completed normally or was cancelled. Once a
* computation has completed, the computation cannot be cancelled.
* If you would like to use a {@code Future} for the sake
* of cancellability but not provide a usable result, you can
* declare types of the form {@code Future<?>} and
* return {@code null} as a result of the underlying task.
*
* <p>
* <b>Sample Usage</b> (Note that the following classes are all
* made-up.)
* <pre> {@code
* interface ArchiveSearcher { String search(String target); }
* class App {
* ExecutorService executor = ...
* ArchiveSearcher searcher = ...
* void showSearch(final String target)
* throws InterruptedException {
* Future<String> future
* = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() {
* public String call() {
* return searcher.search(target);
* }});
* displayOtherThings(); // do other things while searching
* try {
* displayText(future.get()); // use future
* } catch (ExecutionException ex) { cleanup(); return; }
* }
* }}</pre>
*
* The {@link FutureTask} class is an implementation of {@code Future} that
* implements {@code Runnable}, and so may be executed by an {@code Executor}.
* For example, the above construction with {@code submit} could be replaced by:
* <pre> {@code
* FutureTask<String> future =
* new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() {
* public String call() {
* return searcher.search(target);
* }});
* executor.execute(future);}</pre>
*
* <p>Memory consistency effects: Actions taken by the asynchronous computation
* <a href="package-summary.html#MemoryVisibility"> <i>happen-before</i></a>
* actions following the corresponding {@code Future.get()} in another thread.
*
* @see FutureTask
* @see Executor
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's {@code get} method
*/
public interface Future<V> {
/**
* Attempts to cancel execution of this task. This attempt will
* fail if the task has already completed, has already been cancelled,
* or could not be cancelled for some other reason. If successful,
* and this task has not started when {@code cancel} is called,
* this task should never run. If the task has already started,
* then the {@code mayInterruptIfRunning} parameter determines
* whether the thread executing this task should be interrupted in
* an attempt to stop the task.
*
* <p>After this method returns, subsequent calls to {@link #isDone} will
* always return {@code true}. Subsequent calls to {@link #isCancelled}
* will always return {@code true} if this method returned {@code true}.
*
* @param mayInterruptIfRunning {@code true} if the thread executing this
* task should be interrupted; otherwise, in-progress tasks are allowed
* to complete
* @return {@code false} if the task could not be cancelled,
* typically because it has already completed normally;
* {@code true} otherwise
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this task was cancelled before it completed
* normally.
*
* @return {@code true} if this task was cancelled before it completed
*/
boolean isCancelled();
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this task completed.
*
* Completion may be due to normal termination, an exception, or
* cancellation -- in all of these cases, this method will return
* {@code true}.
*
* @return {@code true} if this task completed
*/
boolean isDone();
/**
* Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then
* retrieves its result.
*
* @return the computed result
* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled
* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an
* exception
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
/**
* Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation
* to complete, and then retrieves its result, if available.
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument
* @return the computed result
* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled
* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an
* exception
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
* @throws TimeoutException if the wait timed out
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
- cancel方法: 用来取消任务,如果取消任务成功则返回true,如果取消任务失败则返回false。参数mayInterruptIfRunning表示是否允许取消正在执行却没有执行完毕的任务,如果设置true,则表示可以取消正在执行过程中的任务。如果任务已经完成,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,此方法肯定返回false,即如果取消已经完成的任务会返回false;如果任务正在执行,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为true,则返回true,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为false,则返回false;如果任务还没有执行,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,肯定返回true。
- isCancelled方法: 表示任务是否被取消成功,如果在任务正常完成前被取消成功,则返回true。
- isDone方法:表示任务是否已经完成,若任务完成,则返回true;
- get()方法: 用来获取执行结果,这个方法会产生阻塞,会一直等到任务执行完毕才返回;
get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):用来获取执行结果,如果在指定时间内,还没获取到结果,就直接返回null。
FutureTask