TreeviewCopyright @doctording all right reserved, powered by aleen42
[TOC]
System.arraycopy
使用说明:
/*
* @param src the source array. 源数组
* @param srcPos starting position in the source array. 源数组要复制的起始位置
* @param dest the destination array. 目标数组
* @param destPos starting position in the destination data. 目标数组放置的起始位置;
* @param length the number of array elements to be copied. 要复制的长度
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if copying would cause
* access of data outside array bounds. dest数组大小比src数组大小小会报IndexOutOfBoundsException
* @exception ArrayStoreException if an element in the <code>src</code>
* array could not be stored into the <code>dest</code> array
* because of a type mismatch.
* @exception NullPointerException if either <code>src</code> or
* <code>dest</code> is <code>null</code>.
*/
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
浅拷贝:复制引用
public static void testArraycopy(){
class Obj{
int a;
String b;
public Obj(){
a=0;
b="";
}
public Obj(int _a, String _b){
a= _a;
b=_b;
}
}
int N = 3;
Obj obj1 = new Obj(1, "a");
Obj obj2 = new Obj(2, "b");
Obj obj3 = new Obj(3, "c");
Obj[] st = {obj1, obj2, obj3};
Obj[] dt = new Obj[N];
System.arraycopy(st, 0, dt, 0, N);
// false
System.out.println("两个数组地址是否相同:" + (st == dt));
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
// true
System.out.println("两个数组内容"+i+"是否相同:" + (st[i] == dt[i]));
}
st[0].a = 2;
System.out.println("st[0].a = " + st[0].a);
System.out.println("dt[0].a = " + dt[0].a);
}
/* 输出
两个数组地址是否相同:false
两个数组内容0是否相同:true
两个数组内容1是否相同:true
两个数组内容2是否相同:true
st[0].a = 2
dt[0].a = 2
*/
如下图:拷贝是复制一堆的引用变量到另一个数组,修改副本会影响原来到数组
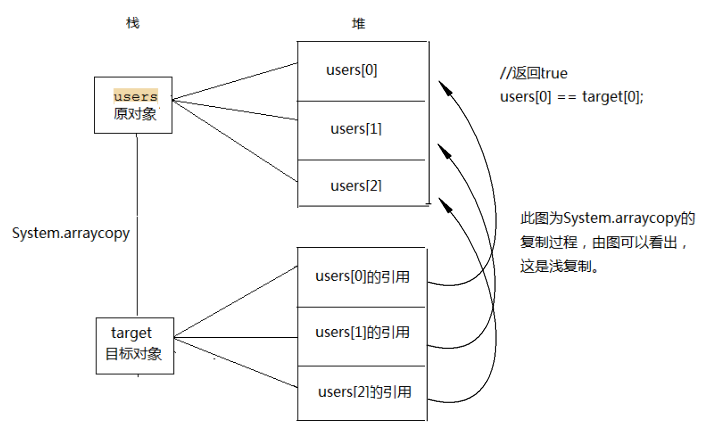
附:深拷贝 & 浅拷贝
- 浅拷贝只是对指针的拷贝,拷贝后两个指针指向同一个内存空间;
- 深拷贝不但对指针进行拷贝,而且对指针指向的内容进行拷贝,经深拷贝后的指针是指向两个不同地址的指针。
对比for效率高
public static void testArrayCopyOfEfficient(){
final int N = 10000;
String[] srcArray = new String[N];
String[] forArray = new String[srcArray.length];
String[] arrayCopyArray = new String[srcArray.length];
//初始化数组
for(int index = 0 ; index < srcArray.length ; index ++){
srcArray[index] = String.valueOf(index);
}
long forStartTime = System.nanoTime();
for(int index = 0 ; index < srcArray.length ; index ++){
forArray[index] = srcArray[index];
}
long forEndTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("for方式复制数组:" + (forEndTime - forStartTime) + "纳秒");
long arrayCopyStartTime = System.nanoTime();
System.arraycopy(srcArray,0,arrayCopyArray,0,srcArray.length);
long arrayCopyEndTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("System.arraycopy复制数组:" + (arrayCopyEndTime - arrayCopyStartTime) + "纳秒");
}
System.arraycopy是直接对内存进行复制,而for循环需要寻址
非线程安全
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @Author mubi
* @Date 2018/11/24 6:00 PM
*/
public class ArrayCopyThreadSafe {
private static int[] arrayOriginal = new int[1024 * 1024 * 10];
private static int[] arraySrc = new int[1024 * 1024 * 10];
private static int[] arrayDist = new int[1024 * 1024 * 10];
private void modify() {
for (int i = 0; i < arraySrc.length; i++) {
arraySrc[i] = i + 1;
}
}
private synchronized void modify2() {
for (int i = 0; i < arraySrc.length; i++) {
arraySrc[i] = i + 1;
}
}
private void copy() {
System.arraycopy(arraySrc, 0, arrayDist, 0, arraySrc.length);
}
private synchronized void copy2() {
System.arraycopy(arraySrc, 0, arrayDist, 0, arraySrc.length);
}
private void copy3() {
synchronized (this) {
System.arraycopy(arraySrc, 0, arrayDist, 0, arraySrc.length);
}
}
private synchronized void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < arraySrc.length; i++) {
arrayOriginal[i] = i + 1;
arraySrc[i] = i;
arrayDist[i] = 0;
}
}
private static void doThreadSafeCheck() throws Exception {
ArrayCopyThreadSafe arrayCopyThreadSafe = new ArrayCopyThreadSafe();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("run count: " + (i + 1));
arrayCopyThreadSafe.init();
Thread threadModify = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.print("modify");
arrayCopyThreadSafe.modify2();
}
});
Thread threadCopy = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.print("copy");
arrayCopyThreadSafe.copy();
}
});
threadModify.start();
Thread.sleep(2);
threadCopy.start();
threadModify.join();
threadCopy.join();
if (!Arrays.equals(arrayOriginal, arrayDist)) {
throw new RuntimeException("System.arraycopy is not thread safe");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
doThreadSafeCheck();
}
}
Array.copyOf
- 直接 new 新的长度,然后调用了
System.arraycopy
/**
* Copies the specified array, truncating or padding with nulls (if necessary)
* so the copy has the specified length. For all indices that are
* valid in both the original array and the copy, the two arrays will
* contain identical values. For any indices that are valid in the
* copy but not the original, the copy will contain <tt>null</tt>.
* Such indices will exist if and only if the specified length
* is greater than that of the original array.
* The resulting array is of exactly the same class as the original array.
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the array
* @param original the array to be copied
* @param newLength the length of the copy to be returned
* @return a copy of the original array, truncated or padded with nulls
* to obtain the specified length
* @throws NegativeArraySizeException if <tt>newLength</tt> is negative
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>original</tt> is null
* @since 1.6
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}