[TOC]
HashMap
数组 + 链表 的实现方式
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map<Integer,String> mp = new HashMap<>(16);
mp.put(1, "a");
mp.put(2, "b");
mp.put(null, null);
mp.put(null, "c");
mp.put(3, null);
System.out.println( Objects.hashCode(null));
mp.entrySet().stream().forEach(m -> {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> keyVal = m;
System.out.println(keyVal.getKey() + ":" + keyVal.getValue());
});
}
}
/*output
0
null:c
1:a
2:b
3:null
*/
数组是HashMap的主体,链表则是主要为了解决哈希冲突而存在的(拉链法解决冲突)
拉链法解决冲突
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size;
// `null`也是有`hashcode`的
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 是否扩容
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 数组中是否有链表
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 数组中的链表遍历
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 链表中存在该key,新值替换旧值
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 是否需要调整数组
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
// 不存在key,旧插入到链表中
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
非线程安全
建议在单线程,不需要同步的时候,用HashMap
HashTable
key,value都不能为null
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map<Integer,String> mp = new Hashtable<>(16);
mp.put(1, "a");
mp.put(2, "b");
// Hashtable key,value不能为null, 否则报`java.lang.NullPointerException`
// mp.put(null, "c");
// mp.put(3, null);
System.out.println( Objects.hashCode(null));
mp.entrySet().stream().forEach(m -> {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> keyVal = m;
System.out.println(keyVal.getKey() + ":" + keyVal.getValue());
});
}
}
/*output
0
2:b
1:a
*/
线程安全
方法都加上了synchronized关键词, synchronized是针对整张Hash表的,即每次锁住整张表让线程独占
底层实现类似Hashmap,也是拉链法

public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
HashMap, Hashtable的区别
HashMap几乎可以等价于Hashtable,除了HashMap是非synchronized的,并可以接受null(HashMap可以接受为null的键值(key)和值(value),而Hashtable则不行)。
HashMap是非synchronized,而Hashtable是synchronized,这意味着Hashtable是线程安全的,多个线程可以共享一个Hashtable;而如果没有正确的同步的话,多个线程是不能共享HashMap的。Java 5提供了
ConcurrentHashMap,它是HashTable的替代,比HashTable的扩展性更好。另一个区别是HashMap的迭代器(Iterator)是
fail-fast迭代器,而Hashtable的enumerator迭代器不是fail-fast的。所以当有其它线程改变了HashMap的结构(增加或者移除元素),将会抛出ConcurrentModificationException,但迭代器本身的remove()方法移除元素则不会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。但这并不是一个一定发生的行为,要看JVM。这条同样也是Enumeration和Iterator的区别。由于Hashtable使用了synchronized,所以在单线程环境下它比HashMap要慢。如果你不需要同步,只需要单一线程,那么使用HashMap性能要好过Hashtable。
HashMap不能保证随着时间的推移Map中的元素次序是不变的。
ConcurrentHashMap(JDK 1.7)
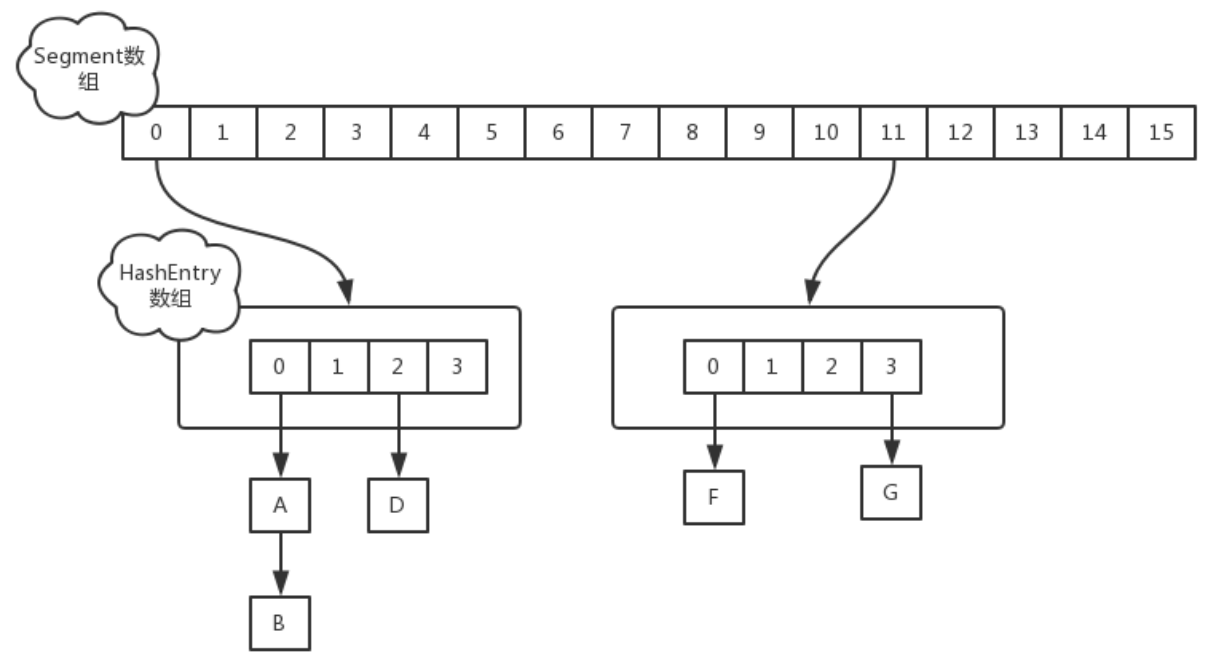
分段的数组+链表实现,线程安全
/**
* The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table.
*/
final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
put
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 第一次 先 hash 定位到 segment 的位置
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
// segment 内部的put方法
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// tryLock 操作
HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
// 找 HashEntry
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
get
hash => Segment => HashEntry => 遍历链表
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Segment<K,V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab;
int h = hash(key);
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
size
并发操作
- 第一种方案他会使用不加锁的模式去尝试多次计算ConcurrentHashMap的size,最多三次,比较前后两次计算的结果,结果一致就认为当前没有元素加入,计算的结果是准确的
第二种方案是如果第一种方案不符合,他就会给每个Segment加上锁,然后计算ConcurrentHashMap的size返回
/**
* Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. If the
* map contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns
* <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>.
*
* @return the number of key-value mappings in this map
*/
public int size() {
// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to
// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
int size;
boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bits
long sum; // sum of modCounts
long last = 0L; // previous sum
int retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retry
try {
for (;;) {
if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation
}
sum = 0L;
size = 0;
overflow = false;
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {
Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j);
if (seg != null) {
sum += seg.modCount;
int c = seg.count;
if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)
overflow = true;
}
}
if (sum == last)
break;
last = sum;
}
} finally {
if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();
}
}
return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;
}
ConcurrentHashMap(JDK 1.8)
Node数组,链表,红黑树
当链表的节点数大于8时会转换成红黑树的结构
put
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//两次hash,减少hash冲突,可以均匀分布
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// 如果i位置没有数据,就直接无锁插入
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// 如果在进行扩容,则先进行扩容操作
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
// 加锁操作,存在hash冲突,锁住链表或者红黑树的头结点
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 表示该节点是链表结构
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 红黑数
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; 链表长度大于8转换为红黑树
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 统计size,并且检查是否需要扩容
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
对比 Jdk1.7
JDK1.8的实现降低锁的粒度,JDK1.7版本锁的粒度是基于Segment的,包含多个HashEntry,而JDK1.8锁的粒度就是HashEntry(首节点)
JDK1.8使用红黑树来优化链表,基于长度很长的链表的遍历是一个很漫长的过程,而红黑树的遍历效率是很快的,代替一定阈值的链表
相对而言
低粒度加锁方式,synchronized并不比ReentrantLock差