[TOC]
JVM
JVM组成
JVM组成:
- 类加载子系统(.class -> loading -> linking -> Initailization)
- 运行时数据区(方法区,堆,thread stack, native statck, pc registor)
- 执行引擎(interpreter, jit compiler, garbage collector; native method interface/Library)
JVM复习要点
- 类加载机制:双亲委派,全盘委托
- 运行时数据区
- GC问题,JVM调优
- 执行引擎Jit等
Hello.class例子
- .java
/**
* @Author mubi
* @Date 2020/9/19 15:51
*/
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 11;
int c = Math.max(a, b);
System.out.println("c:" + c);
}
}
- 反汇编
javap -c Hello.class
Compiled from "Hello.java"
public class Hello {
public Hello();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
Code:
0: bipush 10
2: istore_1
3: bipush 11
5: istore_2
6: iload_1
7: iload_2
8: invokestatic #2 // Method java/lang/Math.max:(II)I
11: istore_3
12: getstatic #3 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
15: new #4 // class java/lang/StringBuilder
18: dup
19: invokespecial #5 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder."<init>":()V
22: ldc #6 // String c:
24: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
27: iload_3
28: invokevirtual #8 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(I)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
31: invokevirtual #9 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
34: invokevirtual #10 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
37: return
}
javap -v
Classfile /Users/mubi/git_workspace/test/java8/src/main/java/Hello.class
Last modified 2020-9-19; size 677 bytes
MD5 checksum 23891c1282b41ccaab435a96e8f3a056
Compiled from "Hello.java"
public class Hello
minor version: 0
major version: 52
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #12.#21 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Methodref #22.#23 // java/lang/Math.max:(II)I
#3 = Fieldref #24.#25 // java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#4 = Class #26 // java/lang/StringBuilder
#5 = Methodref #4.#21 // java/lang/StringBuilder."<init>":()V
#6 = String #27 // c:
#7 = Methodref #4.#28 // java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
#8 = Methodref #4.#29 // java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(I)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
#9 = Methodref #4.#30 // java/lang/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
#10 = Methodref #31.#32 // java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#11 = Class #33 // Hello
#12 = Class #34 // java/lang/Object
#13 = Utf8 <init>
#14 = Utf8 ()V
#15 = Utf8 Code
#16 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#17 = Utf8 main
#18 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
#19 = Utf8 SourceFile
#20 = Utf8 Hello.java
#21 = NameAndType #13:#14 // "<init>":()V
#22 = Class #35 // java/lang/Math
#23 = NameAndType #36:#37 // max:(II)I
#24 = Class #38 // java/lang/System
#25 = NameAndType #39:#40 // out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#26 = Utf8 java/lang/StringBuilder
#27 = Utf8 c:
#28 = NameAndType #41:#42 // append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
#29 = NameAndType #41:#43 // append:(I)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
#30 = NameAndType #44:#45 // toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
#31 = Class #46 // java/io/PrintStream
#32 = NameAndType #47:#48 // println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#33 = Utf8 Hello
#34 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#35 = Utf8 java/lang/Math
#36 = Utf8 max
#37 = Utf8 (II)I
#38 = Utf8 java/lang/System
#39 = Utf8 out
#40 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#41 = Utf8 append
#42 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
#43 = Utf8 (I)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
#44 = Utf8 toString
#45 = Utf8 ()Ljava/lang/String;
#46 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream
#47 = Utf8 println
#48 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)V
{
public Hello();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 5: 0
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=3, locals=4, args_size=1
0: bipush 10
2: istore_1
3: bipush 11
5: istore_2
6: iload_1
7: iload_2
8: invokestatic #2 // Method java/lang/Math.max:(II)I
11: istore_3
12: getstatic #3 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
15: new #4 // class java/lang/StringBuilder
18: dup
19: invokespecial #5 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder."<init>":()V
22: ldc #6 // String c:
24: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
27: iload_3
28: invokevirtual #8 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(I)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;
31: invokevirtual #9 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
34: invokevirtual #10 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
37: return
LineNumberTable:
line 8: 0
line 9: 3
line 10: 6
line 11: 12
line 12: 37
}
SourceFile: "Hello.java"
执行引擎、JIT、逃逸分析
jit工作原理图
在Java的编译体系中,一个Java的源代码文件变成计算机可执行的机器指令的过程中,需要经过两段编译,第一段是把.java文件转换成.class文件;第二段编译是把.class转换成机器指令的过程。
在第二编译阶段,JVM 通过解释字节码将其翻译成对应的机器指令,逐条读入,逐条解释翻译。很显然,经过解释执行,其执行速度必然会比可执行的二进制字节码程序慢很多,这就是传统的JVM的解释器(Interpreter)的功能。为了解决这种效率问题,引入了 JIT(即时编译)技术。
引入了 JIT 技术后,Java程序还是通过解释器进行解释执行,当JVM发现某个方法或代码块运行特别频繁的时候,就会认为这是"热点代码"(Hot Spot Code),然后JIT会把部分"热点代码"翻译成本地机器相关的机器码,并进行优化,然后再把翻译后的机器码缓存起来,以备下次使用。
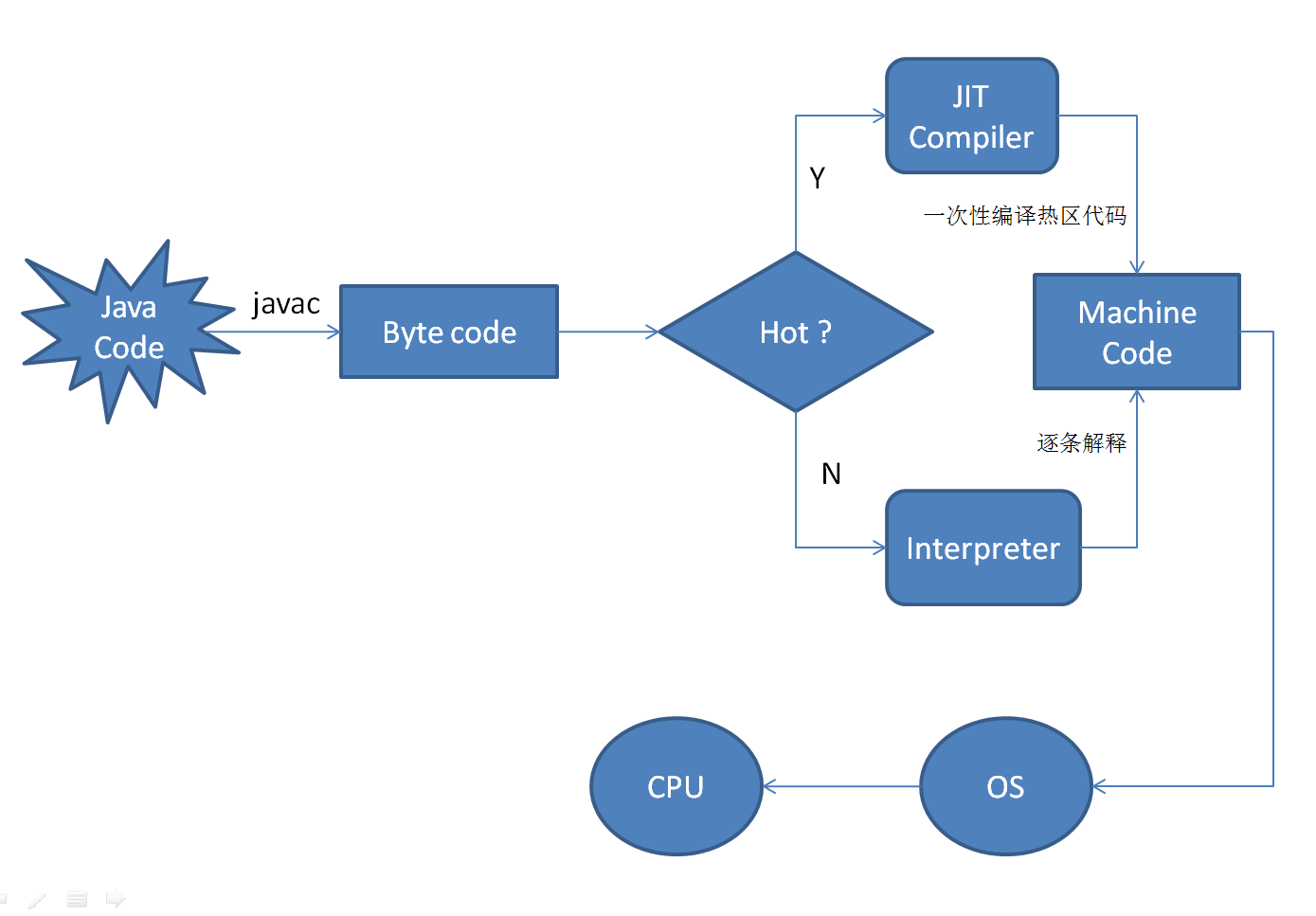
jit如何热点检测
热点检测 上面我们说过,要想触发JIT,首先需要识别出热点代码。目前主要的热点代码识别方式是热点探测(Hot Spot Detection),有以下两种:
基于采样的方式探测(Sample Based Hot Spot Detection) :周期性检测各个线程的栈顶,发现某个方法经常出险在栈顶,就认为是热点方法。好处就是简单,缺点就是无法精确确认一个方法的热度。容易受线程阻塞或别的原因干扰热点探测。
基于计数器的热点探测(Counter Based Hot Spot Detection)。采用这种方法的虚拟机会为每个方法,甚至是代码块建立计数器,统计方法的执行次数,某个方法超过阀值就认为是热点方法,触发JIT编译。
在HotSpot虚拟机中使用的是第二种——基于计数器的热点探测方法,因此它为每个方法准备了两个计数器:方法调用计数器和回边计数器。
- 方法计数器, 就是记录一个方法被调用次数的计数器。
- 回边计数器, 是记录方法中的for或者while的运行次数的计数器。
Jit
JIT编译器(just in time 即时编译器)
JVM(JIT编译启用,默认是启用的))读入.class文件解释后,将其发给JIT编译器;当某个方法或代码块运行特别频繁时,就会把这些代码认定为(Hot Spot Code)热点代码;为了提高热点代码的执行效率,在运行时,虚拟机将会把这些代码编译成与本地平台相关的机器码,并进行各层次的优化
通常JIT的有以下几种手段来优化JVM的性能
- 针对特定CPU型号的编译优化,JVM会利用不同CPU支持的SIMD指令集来编译热点代码,提升性能。像intel支持的SSE2指令集在特定情况下可以提升近40倍的性能。
- 减少查表次数。比如调用Object.equals()方法,如果运行时发现一直是String对象的equals,编译后的代码可以直接调用String.equals方法,跳过查找该调用哪个方法的步骤。
- 逃逸分析。JAVA变量默认是分配在主存的堆上,但是如果方法中的变量未逃出使用的生命周期,不会被外部方法或者线程引用,可以考虑在栈上分配内存,减少GC压力。另外逃逸分析可以实现锁优化等提升性能方法。
- 寄存器分配,部分变量可以分配在寄存器中,相对于主存读取,更大的提升读取性能。
- 针对热点代码编译好的机器码进行缓存。代码缓存具有固定的大小,并且一旦它被填满,JVM 则不能再编译更多的代码。
- 方法内联,也是JIT实现的非常有用的优化能力,同时是开发者能够简单参与JIT性能调优的地方。
作者:huamulou 链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/169d6a50284a 来源:简书 非商业转载
方法内联
函数调用是有一定开销的:保存当前栈,栈操作,函数执行,返回当前栈(call,ret指令等等)。
因此,函数调用需要有一定的时间开销和空间开销,当一个方法体不大,但又频繁被调用时,这个时间和空间开销会相对变得很大,变得非常不划算,同时降低了程序的性能。
方法内联就是把被调用方函数代码"复制"到调用方函数中,来减少因函数调用开销的技术。
eg:被内联前的代码
private int add4(int x1, int x2, int x3, int x4) {
return add2(x1, x2) + add2(x3, x4);
}
private int add2(int x1, int x2) {
return x1 + x2;
}
eg:运行一段时间后,代码被内联翻译成
private int add4(int x1, int x2, int x3, int x4) {
return x1 + x2 + x3 + x4;
}
JVM会自动的识别热点方法,并对它们使用方法内联优化。那么一段代码需要执行多少次才会触发JIT优化呢?通常这个值由-XX:CompileThreshold参数进行设置:
- 使用client编译器时,默认为1500;
- 使用server编译器时,默认为10000;
但是一个方法就算被JVM标注成为热点方法,JVM仍然不一定会对它做方法内联优化。其中有个比较常见的原因就是这个方法体太大了,分为两种情况
- 如果方法是经常执行的,默认情况下,方法大小小于325字节的都会进行内联(可以通过
-XX:MaxFreqInlineSize=N来设置这个大小) - 如果方法不是经常执行的,默认情况下,方法大小小于35字节才会进行内联(可以通过
-XX:MaxInlineSize=N来设置这个大小)
我们可以通过增加这个大小,以便更多的方法可以进行内联;但是除非能够显著提升性能,否则不推荐修改这个参数。因为更大的方法体会导致代码内存占用更多,更少的热点方法会被缓存,最终的效果不一定好。
作者:huamulou 链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/169d6a50284a 来源:简书 非商业转载。
逃逸分析
什么是逃逸分析
在编译程序优化理论中,逃逸分析是一种确定指针动态范围的方法,简单来说就是分析在程序的哪些地方可以访问到该指针
通俗地讲,逃逸分析就是确定一个变量要放堆上还是栈上,规则如下:
- 是否有在其它地方(非局部)被引用。只要有可能被引用了,那么它一定分配到堆上,否则分配到栈上
- 即使没有被外部引用,但对象过大,无法存放在栈区上。依然有可能分配到堆上
逃逸分析实例
public class Rect {
private int w;
private int h;
public Rect(int w, int h) {
this.w = w;
this.h = h;
}
public int area() {
return w * h;
}
public boolean sameArea(Rect other) {
return this.area() == other.area();
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception{
java.util.Random rand = new java.util.Random();
int sameArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100_000_000; i++) {
Rect r1 = new Rect(rand.nextInt(5), rand.nextInt(5));
Rect r2 = new Rect(rand.nextInt(5), rand.nextInt(5));
if (r1.sameArea(r2)) {
sameArea++;
}
}
System.out.println("Same area: " + sameArea);
System.in.read();
}
}
如上代码创建了一亿对随机大小的矩形,并去计算有多少对是大小一样的。每次迭代都会创建一对新的矩形。你可能会认为main方法里会创建2亿个Rect对象:一亿个r1,一亿个r2。
不过,如果某个对象只是在方法内部创建并使用的话:也就是说,它不会传递到另一个方法中或者作为返回值返回;那么运行时程序就还能做得更聪明一些。你可以说这个对象是没有逃逸出去的,因此运行时(其实就是JIT编译器)做的这个分析又叫做逃逸分析。
如果一个对象没有逃逸出去,那也就是说JVM可以针对这个对象做一些类似“栈自动分配”的事情。在这个例子当中,这个对象不会从堆上分配空间,因此它也不需要垃圾回收器来回收。一旦使用这个“栈分配(stack-allocated)”对象的方法返回了,这个对象所占用的内存也就自动被释放掉了。
- escape.hpp
typedef enum {
UnknownEscape = 0,
NoEscape = 1, // An object does not escape method or thread and it is
// not passed to call. It could be replaced with scalar.
ArgEscape = 2, // An object does not escape method or thread but it is
// passed as argument to call or referenced by argument
// and it does not escape during call.
GlobalEscape = 3 // An object escapes the method or thread.
} EscapeState;
如果只看源代码,会认为r1对象是不会逃逸出main方法外的,但r2会作为参数传给r1的sameArea方法,因此它逃逸出了main方法外。
- Java中的方法调用最终会通过编译器替换为字节码invoke。它会把调用目标(也就是接收对象,注:即要调用的对象)和入参填充到栈中,然后查找到这个方法,再分发给它(也就是执行这个方法)。本例子会将:this对象和参数对象r2入栈操作,因此在这个例子中,这意味着如果逃逸分析分析完这段Java代码,r1和r2都会归类为ArgEscape。
本例两个方法的字节码如下:
public int area();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #2 // Field w:I
4: aload_0
5: getfield #3 // Field h:I
8: imul
9: ireturn
public boolean sameArea(Rect);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokevirtual #4 // Method area:()I
4: aload_1
5: invokevirtual #4 // Method area:()I
8: if_icmpne 15
11: iconst_1
12: goto 16
15: iconst_0
16: ireturn
通过JITWatch或者PrintCompilation可以看到,area()方法的调用被内联进了调用方sameArea()方法里,而sameArea()又被内联到了main()方法的循环体中。
现在sameArea()方法和area()方法都被内联进来了,方法域的问题不复存在,所有的变量都只在main方法的作用域内了。也就是说逃逸分析不会再把r1和r2视作ArgEscape类型:方法内联之后,它们现在都被归类为NoEscape。
注:现代JVM中逃逸分析是默认开启的,得通过JVM参数`-XX:-DoEscapeAnalysis`来关掉它。默认-XX:+PrintGCDetails,如下:没有发生gc信息,因为对象是在栈上分配的
Heap
PSYoungGen total 76288K, used 16896K [0x000000076ab00000, 0x0000000770000000, 0x00000007c0000000)
eden space 65536K, 25% used [0x000000076ab00000,0x000000076bb800f8,0x000000076eb00000)
from space 10752K, 0% used [0x000000076f580000,0x000000076f580000,0x0000000770000000)
to space 10752K, 0% used [0x000000076eb00000,0x000000076eb00000,0x000000076f580000)
ParOldGen total 175104K, used 0K [0x00000006c0000000, 0x00000006cab00000, 0x000000076ab00000)
object space 175104K, 0% used [0x00000006c0000000,0x00000006c0000000,0x00000006cab00000)
Metaspace used 2656K, capacity 4490K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K
class space used 286K, capacity 386K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
关闭逃逸分析,如下:由于Eden区空间满了,导致了内存分配失败、需要进行垃圾回收,因此触发了GC事件
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 65536K->432K(76288K)] 65536K->440K(251392K), 0.0006079 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 65968K->368K(76288K)] 65976K->376K(251392K), 0.0004971 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 65904K->352K(76288K)] 65912K->360K(251392K), 0.0004346 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 65888K->320K(76288K)] 65896K->328K(251392K), 0.0008314 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 65856K->336K(74752K)] 65864K->344K(249856K), 0.0004769 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 64336K->320K(62976K)] 64344K->328K(238080K), 0.0009368 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 62784K->32K(61952K)] 62792K->336K(237056K), 0.0004848 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 61472K->32K(60928K)] 61776K->336K(236032K), 0.0005324 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 60448K->32K(75776K)] 60752K->336K(250880K), 0.0008801 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 74784K->0K(73728K)] 75088K->304K(248832K), 0.0005961 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 73216K->0K(72704K)] 73520K->304K(247808K), 0.0003502 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 71680K->0K(70656K)] 71984K->304K(245760K), 0.0003155 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 70144K->32K(69632K)] 70448K->336K(244736K), 0.0003051 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 68640K->32K(67584K)] 68944K->336K(242688K), 0.0003187 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 67104K->32K(66560K)] 67408K->336K(241664K), 0.0006024 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 65568K->32K(64512K)] 65872K->336K(239616K), 0.0003106 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 64032K->32K(62976K)] 64336K->336K(238080K), 0.0003399 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 62496K->32K(61952K)] 62800K->336K(237056K), 0.0011022 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 61472K->32K(60928K)] 61776K->336K(236032K), 0.0004817 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 60448K->32K(59904K)] 60752K->336K(235008K), 0.0014253 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 59424K->32K(58880K)] 59728K->336K(233984K), 0.0003223 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 58400K->0K(57856K)] 58704K->304K(232960K), 0.0005910 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 57344K->0K(80896K)] 57648K->304K(256000K), 0.0010148 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 80384K->32K(78848K)] 80688K->336K(253952K), 0.0004962 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 78368K->32K(96256K)] 78672K->336K(271360K), 0.0017178 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 95776K->0K(102400K)] 96080K->304K(277504K), 0.0003609 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 101888K->0K(99328K)] 102192K->304K(274432K), 0.0004847 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 98816K->32K(96768K)] 99120K->336K(271872K), 0.0009419 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 96288K->0K(94208K)] 96592K->304K(269312K), 0.0011469 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 93696K->0K(91648K)] 94000K->304K(266752K), 0.0003447 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 91136K->0K(89088K)] 91440K->304K(264192K), 0.0003101 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 88576K->0K(87040K)] 88880K->304K(262144K), 0.0003009 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 86528K->32K(84992K)] 86832K->336K(260096K), 0.0002912 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 84512K->32K(82944K)] 84816K->336K(258048K), 0.0003761 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 82464K->32K(80896K)] 82768K->336K(256000K), 0.0003003 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 80416K->0K(78848K)] 80720K->304K(253952K), 0.0008583 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 78336K->0K(98816K)] 78640K->304K(273920K), 0.0019932 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 98304K->0K(102400K)] 98608K->304K(277504K), 0.0010039 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 101888K->0K(99328K)] 102192K->304K(274432K), 0.0003314 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 98816K->32K(96768K)] 99120K->336K(271872K), 0.0003248 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 96288K->0K(94208K)] 96592K->304K(269312K), 0.0006550 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 93696K->0K(91648K)] 94000K->304K(266752K), 0.0003535 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 91136K->0K(89088K)] 91440K->304K(264192K), 0.0003432 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 88576K->0K(87040K)] 88880K->304K(262144K), 0.0003652 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 86528K->32K(84992K)] 86832K->336K(260096K), 0.0004546 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 84512K->32K(82944K)] 84816K->336K(258048K), 0.0004582 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 82464K->32K(80896K)] 82768K->336K(256000K), 0.0007312 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 80416K->0K(78848K)] 80720K->304K(253952K), 0.0003692 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
The daemon will cancel the build.
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 78336K->0K(76800K)] 78640K->304K(251904K), 0.0004797 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 76288K->0K(74752K)] 76592K->304K(249856K), 0.0003395 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 74240K->0K(73216K)] 74544K->304K(248320K), 0.0003104 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 72704K->32K(71680K)] 73008K->336K(246784K), 0.0003212 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 71199K->0K(70144K)] 71504K->304K(245248K), 0.0010164 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 69632K->32K(68608K)] 69936K->336K(243712K), 0.0002929 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 68128K->32K(67072K)] 68432K->336K(242176K), 0.0004349 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 66592K->0K(65536K)] 66896K->304K(240640K), 0.0003044 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 65024K->0K(64000K)] 65328K->304K(239104K), 0.0007509 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 63488K->0K(62464K)] 63792K->304K(237568K), 0.0003197 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 61952K->0K(61440K)] 62256K->304K(236544K), 0.0009580 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 60928K->0K(73728K)] 61232K->304K(248832K), 0.0010298 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 73216K->32K(72192K)] 73520K->336K(247296K), 0.0003024 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
Same area: 18079262
Heap
PSYoungGen total 72192K, used 60243K [0x000000076ab00000, 0x0000000770f80000, 0x00000007c0000000)
eden space 71680K, 84% used [0x000000076ab00000,0x000000076e5ccd50,0x000000076f100000)
from space 512K, 6% used [0x0000000770e80000,0x0000000770e88000,0x0000000770f00000)
to space 512K, 0% used [0x0000000770f00000,0x0000000770f00000,0x0000000770f80000)
ParOldGen total 175104K, used 304K [0x00000006c0000000, 0x00000006cab00000, 0x000000076ab00000)
object space 175104K, 0% used [0x00000006c0000000,0x00000006c004c050,0x00000006cab00000)
Metaspace used 2656K, capacity 4490K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K
class space used 286K, capacity 386K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
happends-before规则
happens-before原则定义如下:
- 如果一个操作happens-before另一个操作,那么第一个操作的执行结果将对第二个操作可见,而且第一个操作的执行顺序排在第二个操作之前。
- 两个操作之间存在happens-before关系,并不意味着一定要按照happens-before原则制定的顺序来执行。如果重排序之后的执行结果与按照happens-before关系来执行的结果一致,那么这种重排序并不非法。
具体规则:
- 程序次序规则:一个线程内,按照代码顺序,书写在前面的操作先行发生于书写在后面的操作;
- 锁定规则:一个unLock操作先行发生于后面对同一个锁额lock操作;
- volatile变量规则:对一个变量的写操作先行发生于后面对这个变量的读操作;
- 传递规则:如果操作A先行发生于操作B,而操作B又先行发生于操作C,则可以得出操作A先行发生于操作C;
- 线程启动规则:Thread对象的start()方法先行发生于此线程的每个一个动作;
- 线程中断规则:对线程interrupt()方法的调用先行发生于被中断线程的代码检测到中断事件的发生;
- 线程终结规则:线程中所有的操作都先行发生于线程的终止检测,我们可以通过Thread.join()方法结束、Thread.* isAlive()的返回值手段检测到线程已经终止执行;
- 对象终结规则:一个对象的初始化完成先行发生于他的finalize()方法的开始;